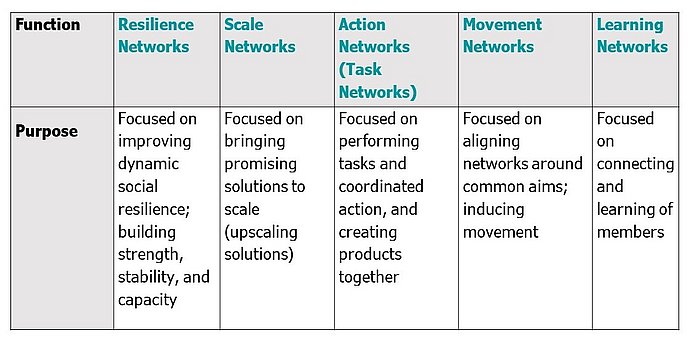
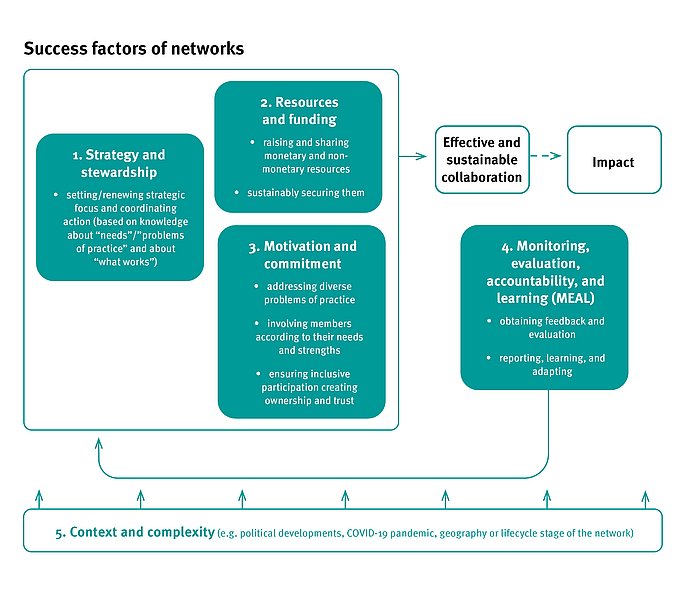
For precise examples for these factors, based on the peer networks’ cases, see the learning paper from page 16.
Networks as agents of change
Members of IDoS are convinced that global developments and the demands for quality education arising thereof can best be tackled in association with others, sharing experiences across borders and learning from each other. The systematic and regular exchange of globally available knowledge and practices on the topic of early STEM Education in a changing world and collective learning is critical to achieving impact. IDoS peers pave the way for networks to become 'education ecosystems': supporting and impacting national education policies, increasing the capacity of teachers and educators, and improving access to STEM Education worldwide. IDoS peers share a common vision of educational innovation, whereby STEM Education concepts are developed, professionalised, and effectively implemented in networks of different countries in a way that is tailored to local needs on the ground.
The authors of the paper conclude that impact networks designed to support early STEM Education – such as those described by the IDoS peers – play an important role in advancing childrens’ understanding of and actions towards the complex, rapidly changing conditions of the world. If successful, such networks can create a culture of sustainability – meeting the critical needs of the present on both a local and global scale, without compromising the needs of the future.